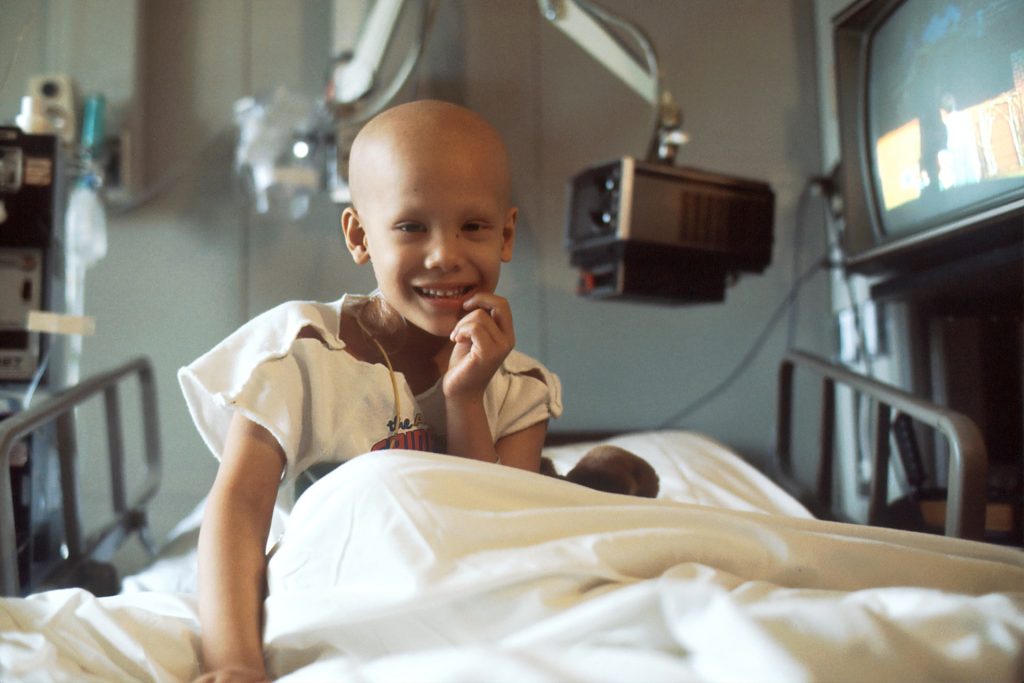
Could Possible Budget Cuts Cost Cancer Patients’ Lives?

The Department of Health’s 2025/26 Budget Vote is expected to focus on addressing the shortfall caused by the withdrawal of international funding from programmes combating communicable diseases such as HIV and TB. But as non-communicable diseases like blood cancer surpass infectious diseases, redirecting resources could further cripple screening, diagnosis, and treatment – putting more lives at risk.
Too Few Resources, Too Many Lives Lost
Palesa Mokomele, Head of Community Engagement and Communications at DKMS Africa, highlights the difficulties faced by blood cancer patients within the country’s healthcare system. “Nearly 80% of South Africans rely on a system already operating at full capacity, with many left with little more than hope due to limited access to care. Even before these new funding shifts, resources for blood cancer detection and treatment were critically scarce, contributing to the loss of more than 4000 lives each year.”
Illustrating how a lack of medical infrastructure creates additional barriers to life-saving care, she says, “The survival rate for a stem cell transplant is up to 50% with a matched unrelated donor and 61% with a matched related donor. Yet many healthcare facilities simply don’t have the resources to perform these procedures. As a result, most patients receive only medical management, which may not be enough to ensure survival. Given our population size, transplant activity remains critically low – only 139 of the required 600 transplants are performed on adults annually, and just 18 of the 250 needed for children.”
Finances Dictate Healthcare Choices
Beyond the overstretched and under-resourced public health sector, the financial burden on patients remains a major obstacle. “One in five South African households delays seeking healthcare simply because they cannot afford it,” notes Mokomele. “While the state covers the cost of a stem cell transplant from a matching donor, other essential expenses such as tissue typing, donor searches, and stem cell procurement are not covered. These out-of-pocket costs place treatment out of reach for many, leading to heartbreaking decisions and poorer outcomes.”
She adds that socio-economic challenges often make accessing care even harder for patients. “Being the sole breadwinner means some individuals struggle to take time off work for necessary treatment. In other cases, mothers face the impossible choice between continuing their own treatment or staying home to care for their children when no other support is available.”
Post-transplant Survival Challenges
Even for patients who manage to undergo a transplant, their survival remains at risk due to conditions in some public healthcare facilities. “Overcrowding and poor sanitation create dangerous environments for these highly immunocompromised patients,” warns Mokomele. “To safeguard their fragile health, they need access to clean water, proper sanitation, isolation, and balanced nutrition.”
She stresses that long recovery periods make it difficult for patients from distant areas to complete their care without proper housing at treating hospitals. “Without these accommodations, many are forced to abandon treatment, putting their survival at risk.”
“No patient should be denied life-saving treatment due to funding constraints. We urge government and the private sector to collaborate in strengthening blood cancer care, and we encourage the public to play their part by supporting fundraising initiatives that help bridge critical gaps in treatment access,” concludes Mokomele.
Go to https://www.dkms-africa.org/get-involved/donate-money to contribute to this cause.