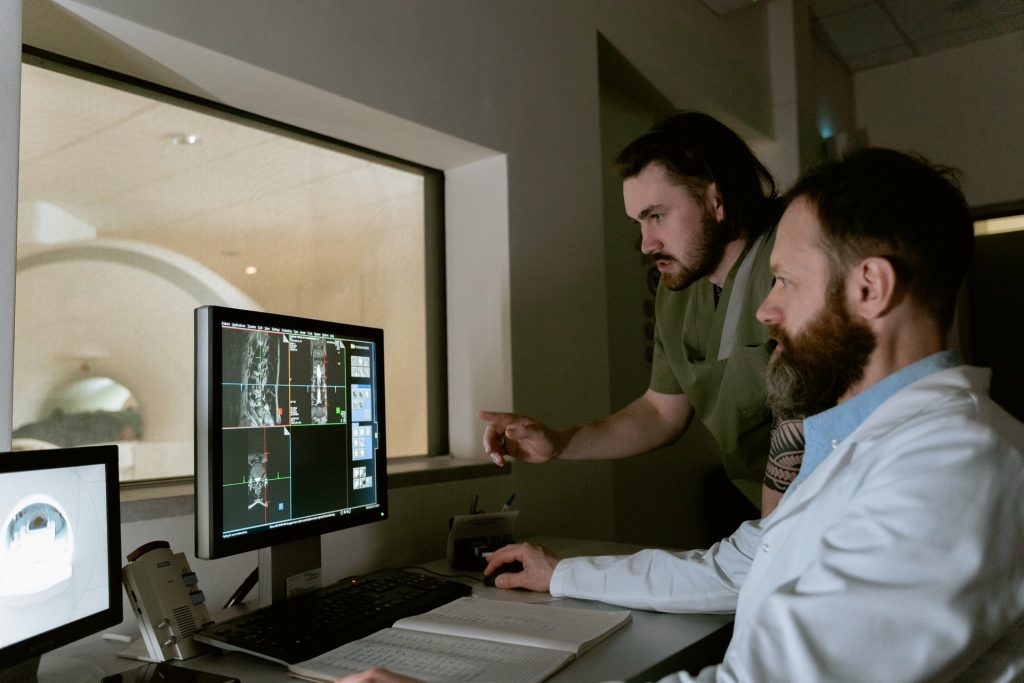
Antiepileptics in Comatose Cardiac Arrest Survivors are Ineffective, Study Shows
A large scale study of comatose intensive care (ICU) patients admitted after cardiac arrest and resuscitation has shown that antiepileptics to treat epilepsy-like brain activity has no effect, and may even prolong ICU stay.
Following a cardiac arrest and resuscitation, patients may need an ICU stay, and are in a coma. By that stage, the cardiac arrest may have damaged the brain to such an extent that half of the patients will not recover from coma. The other half will also have permanent damage, for example of memory functions. It is extremely difficult to predict if a patient will awaken and what their prognosis is, so clinicians make use of EEG (electroencephalography).
In 10–20% of the patients admitted to the ICU after cardiac arrest and resuscitation, there are signs of brain activity that appear similar to epilepsy: unlike an attack this activity is continuous. For a long time, it was unclear if anti-epileptic medication could help better recovery. As a result, some patients received this medication and some did not.
Now, a large-scale study done between 2014 and 2021 on 172 patients has proven that this medication is ineffective: it does not help recovery, even necessitating a longer ICU stay. The researchers, led by Professor Jeannette Hofmeijer of the University of Twente and Rijnstate Hospital in Arnhem, published their findings in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The conclusion from this study is that anti-epileptic medication does not lead to an improved recovery. The findings show that patients may need to stay longer at the ICU: for the patient an undesired situation, and it puts extra pressure on the health care system.
Aside from patients who show continuous epileptic signals, a small group of patients show signs of a typical epileptic seizure: a short and heavy attack. In these situations, anti-epileptics could help, but this still needs further research.
“Although the outcome of the trial may be disappointing in terms of chances of recovery, it also takes away uncertainties from the family. The signals point at serious brain damage that would lead to a much longer stay at the ICU,” said Prof Hofmeijer.
Source: University of Twente