Removing Fallopian Tubes during Other Abdominal Surgeries may Lower Ovarian Cancer Risk
Mathematical modelling study suggests this approach could also reduce total healthcare costs in Germany
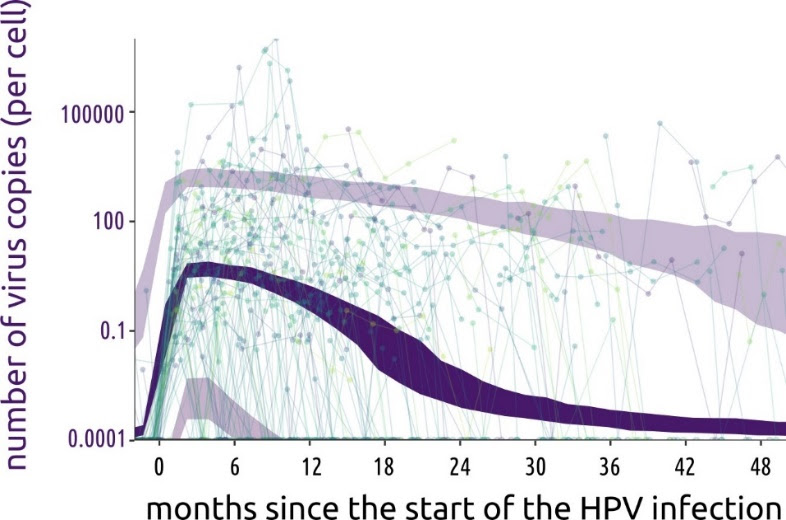
A mathematical modelling study conducted in Germany suggests that ovarian cancer incidence could be reduced and healthcare savings boosted if women who have already completed their families were offered fallopian tube removal during any other suitable abdominal surgeries. Angela Kather and Ingo Runnebaum of Jena University Hospital, Germany, and colleagues present these findings on January 30th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
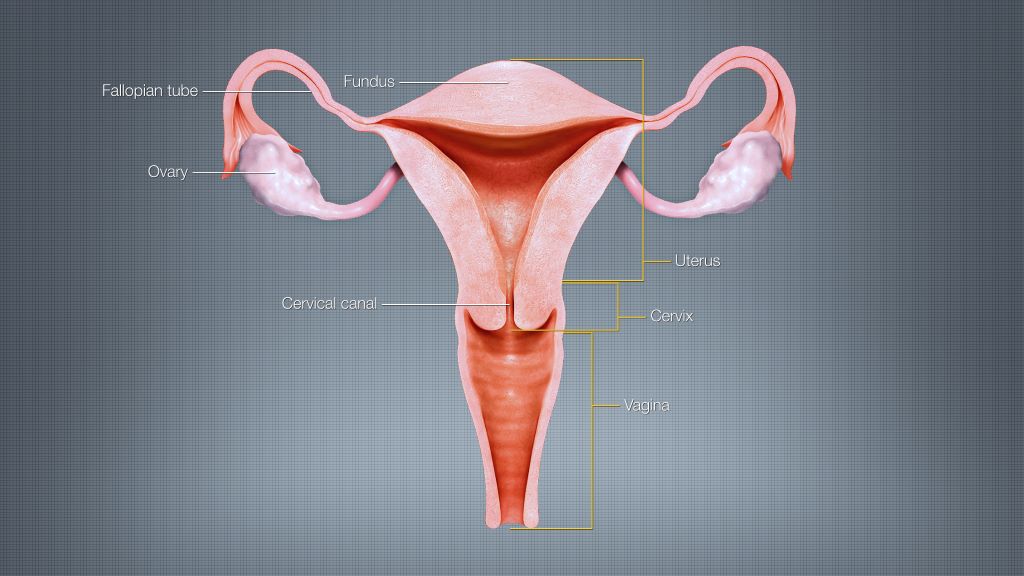
Some of the most widespread and serious forms of ovarian cancer begin in the fallopian tubes, and removing them may reduce ovarian cancer risk. While women at average risk of ovarian cancer are not recommended to have surgery solely to remove their fallopian tubes, many surgeons offer “opportunistic” tube removal during other gynaecologic surgeries such as hysterectomy or tubal sterilisation. Opportunistic removal may also be feasible during other abdominal surgeries, such as gallbladder removal.
However, the overall potential benefits of opportunistic fallopian tube removal have been unclear. To help clarify, Kather and colleagues developed a mathematical model that incorporates real-world patient statistics to predict population-level risks of ovarian cancer after opportunistic fallopian tube removal, as well as the potential healthcare cost savings.
By applying the model to statistics from Germany, the researchers predicted that opportunistic fallopian tube removal during every hysterectomy and tubal sterilisation could reduce ovarian cancer cases by 5% across the female population of Germany. Removal during every suitable abdominal surgery for women who are done having children could reduce nationwide cancer cases by 15%, the analysis suggests, and it could save more than €10 million in healthcare costs annually.
Ovarian cancer is the third most common gynaecologic cancer in the world and has a mortality rate of 66%. Overall, these findings suggest that opportunistic fallopian tube removal during appropriate abdominal surgeries could not only lower population-level ovarian cancer risks and prevent ovarian cancer deaths, but also provide economic benefits. This study could help inform health policy and insurance costs for the procedure.
The authors add, “We developed a mathematical model to estimate the likelihood of women undergoing surgeries that offer an opportunity for fallopian tube removal and the potential for reducing their ovarian cancer risk. Applying this model to the entire female population of Germany revealed that 15% of ovarian cancer cases could be prevented if fallopian tubes were removed during every suitable abdominal surgery in women who have completed their families. This approach has the potential to extend healthy years of life and significantly save healthcare costs.”
Provided by PLOS