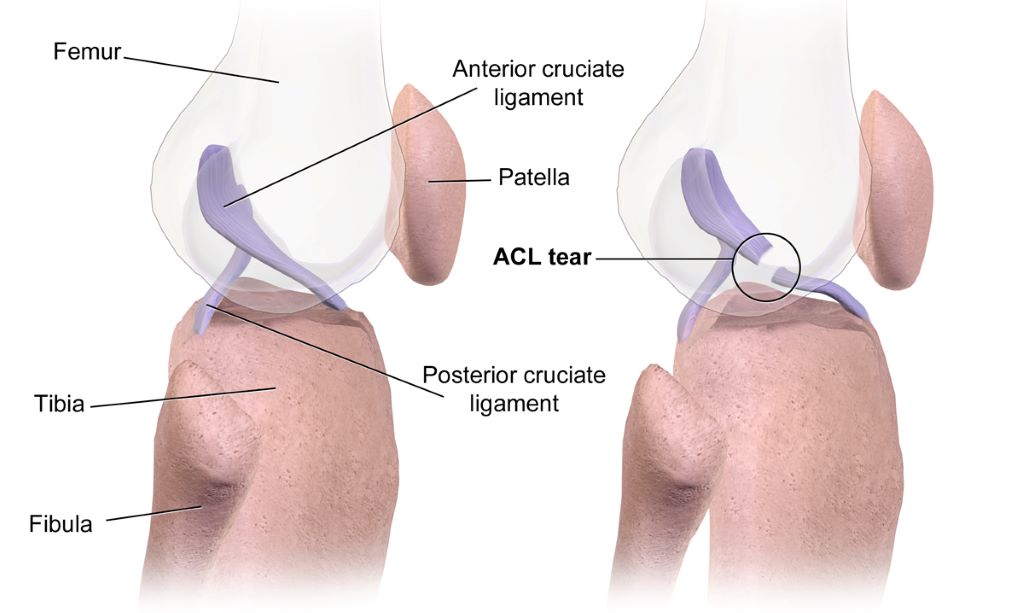
Non-genetic Theories of Cancer Address Inconsistencies in Current Paradigm
A recent essay argues for re-considering cancer as a genetic disease
It’s time for researchers to reconsider the current paradigm of cancer as a genetic disease, argued Sui Huang from the Institute for Systems Biology, USA, and colleagues in a new essay published March 18th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
The prevailing theory on the origin of cancer is that an otherwise normal cell accumulates genetic mutations that allow it to grow and reproduce unchecked. This paradigm has driven large-scale cancer genome sequencing projects, such as The Cancer Genome Atlas, to identify cancer-driving mutations and develop drugs designed to target aberrant proteins and pathways.
In their new essay, Huang and colleagues argue that this somatic mutation theory of cancer is unproductive. They point to inconsistencies in the sequencing data that contradict the current theory, including the fact that many cancers have no known driver mutations while some normal tissues can harbour cancer-causing mutations.
They propose a broader, more “holistic” view that embraces organismal biology and theory. Specifically, they encourage considering alternative paradigms that encompass non-genetic processes involved in tumorigenesis. For example, they explain the concepts of cancer as a result of disruptions in gene regulatory networks (Huang) — or of tissue organisation, a theory that considers the disturbance of the field generated by neighbouring cells and surrounding tissue (Soto-Sonnenschein). The authors argue that these alternative explanations will guide experiments to advance our understanding of the origins of cancer.
The authors add: “A full embrace of the idea that the origin of cancer lies beyond the realm of genetic mutations will open new vistas on cancer treatment and prevention. Accepting that not all carcinogens are mutagens will strengthen public health policies aimed to prevent exposure to environmental non-mutagenic factors that may promote cancer, such as food additives and plastics and many other toxicants that alter tissue homeostasis.”
Provided by PLOS