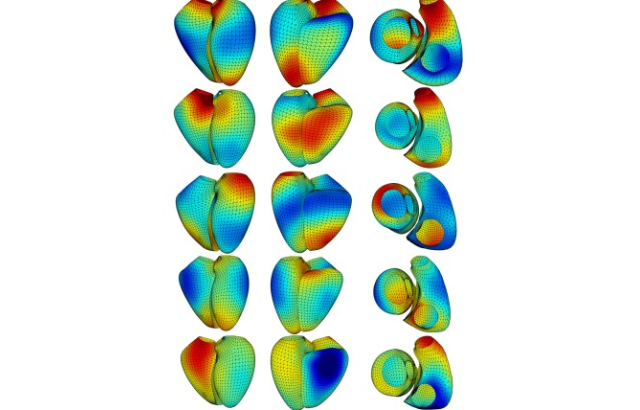
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London and other universities have for the first time examined the genetic basis of the heart’s left and right ventricles using advanced 3D imaging and machine learning.
Prior research primarily focused on the heart’s size and volume and specific chambers. By studying both ventricles together, the team was able to capture the more intricate, multi-dimensional aspects of the heart shape.
This new approach of exploring shape has led to the discovery of new heart-associated genes and provided a better understanding of the biological pathways linking heart shape to cardiovascular disease.
Cardiovascular disease is among the leading causes of death in the UK and globally. The findings of this study could change how cardiac disease risk is evaluated. Genetic information related to heart shape can provide a risk score for heart disease, offering potentially early and more tailored assessment in clinical settings.
“This study provides new information on how we think about heart disease risk,” said Patricia B. Munroe, Professor of Molecular Medicine at Queen Mary and co-author of the study. “We’ve long known that size and volume of the heart matter, but by examining shape, we’re uncovering new insights into genetic risks. This discovery could provide valuable additional tools for clinicians to predict disease earlier and with more precision.”
The team used cardiovascular MRI images from over 40 000 individuals from the UK Biobank to create 3D models of the ventricles. Through statistical analysis, they identified 11 shape dimensions that describe the primary variations in heart shape.
Subsequent genetic analysis found 45 specific areas in the human genome linked to different heart shapes. Fourteen of these areas had not been previously known to influence heart traits.
“This study sets an important foundation for the exploration of genetics in both ventricles”, said Dr Richard Burns, Statistical Geneticist at Queen Mary. “The study confirms that combined cardiac shape is influenced by genetics, and demonstrates the usefulness of cardiac shape analysis in both ventricles for predicting individual risk of cardiometabolic diseases alongside established clinical measures.”
This research marks an exciting new chapter in understanding how genetics influence the heart and opens the doors to further studies on how these findings could be integrated into clinical practice, ultimately benefiting millions at risk of heart disease.
Source: Queen Mary University of London

