Periods of Hypoglycaemia Worsen Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy
People with diabetes who experience periods of hypoglycaemia, a common event in those new to blood sugar management, are more likely to have worsening diabetic eye disease. Now, researchers say they have linked such low blood sugar levels with a molecular pathway that is activated in hypoxic cells in the eye.
The research, involving human and mouse eye cells and intact retinas grown in a low glucose environment in the laboratory, as well as mice with low glucose levels, was published in Cell Reports.
“Temporary episodes of low glucose happen once or twice a day in people with insulin-dependent diabetes and often among people newly diagnosed with the condition,” says Akrit Sodhi, MD, PhD, Johns Hopkins Medicine professor. Low glucose levels can also occur during sleep in people with non-insulin dependent diabetes. “Our results show that these periodic low glucose levels cause an increase in certain retinal cell proteins, resulting in an overgrowth of blood vessels and worsening diabetic eye disease,” adds Sodhi.
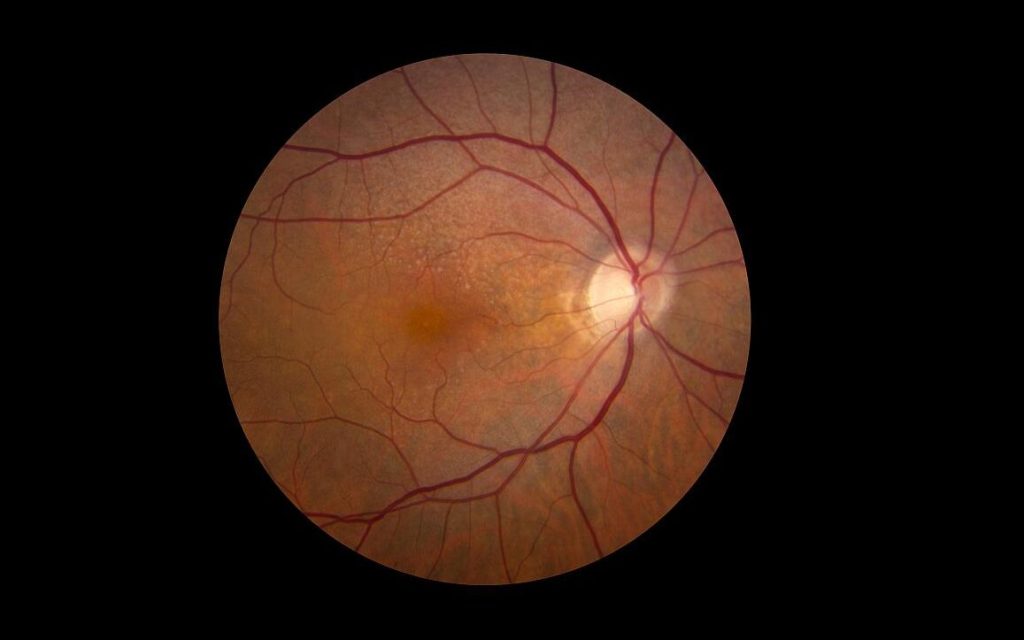
Up to a third of diabetic patients will develop diabetic retinopathy, which is characterised by the overgrowth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
Sodhi says the current study suggests that people with diabetic retinopathy may be particularly vulnerable to periods of low glucose, and keeping glucose levels stable should be an important part of glucose control.
For the study, the researchers analysed protein levels in human and mouse retinal cells and intact retinas grown in an environment of low glucose in the laboratory, as well as in mice that had occasional low blood sugar.
In human and mouse retinal cells, low glucose levels triggered a cascade of molecular changes that can lead to blood vessel overgrowth. First, the researchers saw that low glucose caused a decrease in retinal cells’ ability to break down glucose for energy.
When the researchers focused on Müller glial cells, which are supportive cells for neurons in the retina and rely primarily on glucose for energy production, they found that the cells increased the expression of the GLUT1 gene, which makes a protein that transports glucose into cells.
The researchers found that, in response to low glucose, the cells increased levels of a transcription factor, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α. This turned on the cellular machinery, including GLUT1, needed to improve their ability to utilise available glucose, preserving the limited oxygen available for energy production by retinal neurons.
However, in hypoxic environments, as occurs in the retinas of patients with diabetic eye disease, this normal, physiologic response to low glucose triggered a flood of HIF-1α protein into the nucleus.
This resulted in an increase in the production of proteins such as VEGF and ANGPTL4, which cause the growth of abnormal, leaky blood vessels – the key culprit of vision loss in people with diabetic eye disease.
The researchers plan to study whether low glucose levels in people with diabetes may impact similar molecular pathways in other organs, such as the kidney and brain.
Sodhi says the HIF-1α pathway may serve as an effective target for developing new treatments for diabetic eye disease.
Source: Johns Hopkins Medicine