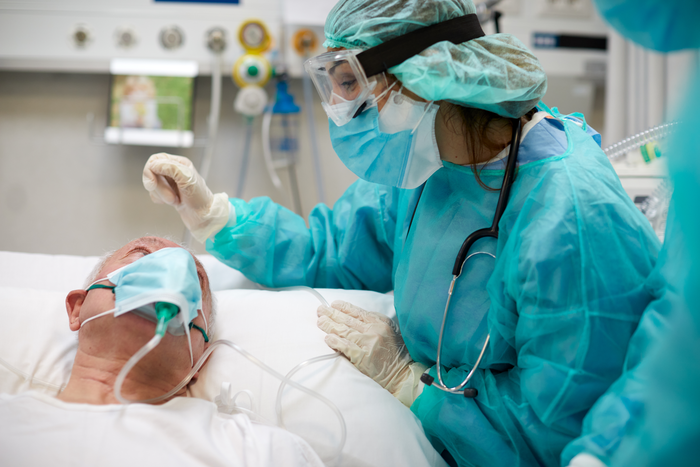
In stark contrast to South Africa’s approach to COVID and the country’s experts characterising Omicron as “mild”, US experts have said that calling it “mild” ignores the harsh situation their country faces: record hospitalisations, sick children, other conditions being worsened by COVID, and staff shortages.
While Omicron’s odds of causing a person’s hospitalisation or death are lower, US numbers suggest that Omicron is, in fact, serious on a population level.
“What’s mild about hospitals at or near the breaking point? What’s mild about hundreds of healthcare workers per hospital out ill with COVID? What’s mild about 1.3 million cases in the U.S. just yesterday? What’s mild about the rising titer of burnout? What’s mild about an unprecedented number of children now ill and hospitalised with COVID?” Clyde Yancy, MD, chief of cardiology at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, wrote in an email to MedPage Today.
“I think prudence would suggest that we reframe ‘mild’ and think more about ‘self-limited,'” he added. “We are likely at or near a plateau but how long will it last and how much more agony awaits?”
Americans were hospitalised in record numbers last week. “When there are many more people sick in large numbers – in millions – even if it’s a smaller percentage that’s going to be severely sick, that is going to result in large numbers in the hospitals,” said Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
While Omicron is still a threat for those unvaccinated or without previous infection, its high breakthrough rate is a cause for concern, especially in vulnerable people.
“Individuals who have breakthroughs after being vaccinated, including the elderly who have comorbid heart disease, are now flooding our emergency departments with decompensated cardiovascular diagnoses and a positive coronavirus test,” said cardiologist Jim Januzzi, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston.
As well as buckling healthcare systems, vulnerable and overlooked populations are being affected by Omicron even more.
Paediatric hospitalisations in the US reached a new peak in mid-January, with 20% of the entire pandemic’s hospitalisations of children happening in just two weeks in January. Over 1000 children have died from COVID by the CDC’s numbers, including 359 under five.
Moreover, patients on immunosuppressive medications may be less protected by the vaccines. “The labelling of the Omicron infection as ‘mild’ overlooks the important features and the messaging to the public,” rheumatologist Vaidehi Chowdhary, MBBS, MD, DM, of Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, wrote in an email to MedPage Today.
“Some patients who are on strong immunosuppressive medications do not have adequate vaccine titers and remain vulnerable,” she said, pointing out that there’s a shortage of monoclonal antibodies and antivirals, which means that this group must take extra precautions to ensure they aren’t infected in the first place.
Omicron’s impact on those who are immunosuppressed or have long COVID is not yet known, Dr Chowdhary noted. “For immunosuppressed patients, to minimise infections, many in-person appointments have been converted to telehealth or elective procedures deferred. The impact of these practices and their impact on overall patient health are not known.”
People living with disabilities and chronic illnesses continue to be faced with worsened infections, delaying consultations and difficulty accessing healthcare.
Then there are those whose infection has exacerbated their condition, whatever it may be. Omicron could be the thing that tips them over the edge, or that keeps them in the hospital for longer, experts have said. Examples seen include patients with blood clots having those clots exacerbated by COVID, and COVID-positive trauma patients having complications and longer recovery times.
Healthcare workers falling ill due to Omicron has seriously stressed US healthcare, with staff shortages have been reported in almost 20% of the country’s hospitals, leaving their already overworked colleagues to work extra.
Dr Januzzi’s hospital has been “completely full, with a huge number of individuals with COVID. So, we’re really at a breaking point where staff are getting sick. Patients and physicians alike are exhausted … the hope would be that we can get through this time and get to the other side of this.”
Source: MedPage Today

